· Alex · securitys · 14 min read
Exploring OWASP Top 10 2021
Dive into each of entry of OWASP Top 10 2021, discussing risks and mitigations

OWASP Top 10 2021
A01:2021 - Broken Access Control
Broken access control basically means that an application isn’t doing a great job of managing who gets to do what. So, some users might end up with access to stuff they shouldn’t. There are a few ways this can happen, and we’re going to run through some of the most common ones:
- Insecure direct object references (IDOR) - When an attacker can access data or resources they shouldn’t by manipulating an identifier (like a URL or user ID).
- Missing function level access control - When the app doesn’t properly check if a user has the right permissions before letting them use a specific feature.
- Forced browsing - When an attacker can reach restricted areas of an app just by guessing the URL or manipulating it.
- Insecure API access control - When the app fails to control access to its APIs, letting unauthorized users make requests or access sensitive data.
So, why should we care about broken access control? Well, it’s simple: it can put sensitive data at risk and allow attackers to wreak havoc on your app. Definitely not a good look for your business! Now, here’s the good news: there are ways to prevent broken access control issues. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
- Role-based access control (RBAC) - Implement a solid system that grants access based on a user’s role, ensuring that users only have access to what they need.
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC) - Take it a step further by defining access rules based on user attributes, like their location, job title, or department.
- Secure token-based authentication - Use tokens to manage user sessions and make sure they’re securely stored and transmitted.
- Regular security audits and monitoring - Keep an eye on your app to make sure everything’s running smoothly and catch any access control issues before they turn into big problems.
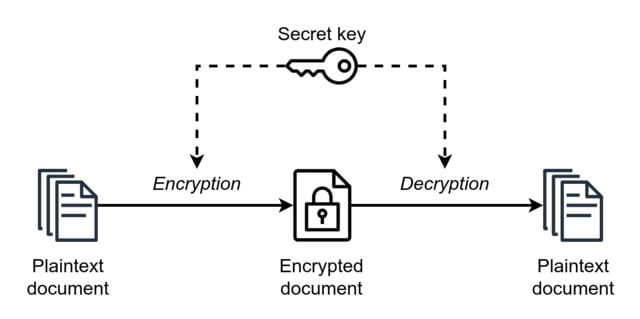
A02:2021 - Cryptographic Failures
Let’s dive into the next vulnerability on the OWASP Top 10 2021 list: Cryptographic Failures. So, what exactly is a cryptographic failure? It’s when an application doesn’t quite nail its cryptographic practices, making it easy for attackers to steal or tamper with sensitive data. This can happen in a few different ways:
- Insecure cryptographic storage - This is when data isn’t stored securely, meaning it’s not encrypted or it’s encrypted using weak algorithms. This can lead to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Insufficient transport layer protection - This is when data isn’t properly protected during transmission between the client and the server. Attackers can intercept and manipulate this data, causing all sorts of chaos.
- Weak key management - This is when cryptographic keys aren’t generated, stored, or retired securely.
When cryptography goes wrong, it can lead to data breaches, loss of customer trust, and even hefty fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations. Here are some best practices to help you avoid these pesky cryptographic failures and keep your app’s data safe and sound:
- Data encryption standards - Always use strong, up-to-date encryption algorithms and protocols to protect your data, both in storage and transit. AES-256 and TLS 1.3 are some solid options, just to name a couple.
- Secure key management strategies - Treat your cryptographic keys like the precious treasures they are. Generate, store, and retire them securely, and make sure they’re only accessible to authorized users.
- Regularly updated cryptographic libraries - Keep your cryptographic libraries up to date to stay ahead of vulnerabilities and exploits. Security is an ever-evolving game, and you’ve got to stay on your toes!
A03:2021 - Injection
Injection attacks happen when an attacker sends malicious data to an application, tricking it into executing unintended commands or accessing unauthorized data.
- SQL injection - This is when an attacker slips some malicious SQL code into a user input field, tricking the app into running unauthorized database queries. This can lead to data leaks, unauthorized data modification, or even full-on database takeovers.
- Command injection - This is when an attacker injects commands into an application that end up being executed on the underlying operating system. This can give the attacker control over the server, allowing them to do all sorts of damage.
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) - This is when an attacker injects malicious scripts into a website, which then gets executed in the user’s browser. This can lead to stolen session cookies, manipulated web content, or even drive-by malware downloads.
I’ve wrote a separate post for defenses against injection vulnerabilities. But I’m going to mention a few best practices here to help you keep injection attacks at bay:
- Input validation - Make sure you’re checking all user inputs for suspicious characters or patterns before processing them.
- Parameterized queries - Use parameterized queries or prepared statements in your code when dealing with databases. This helps ensure that user input is treated as data, not as part of the SQL query itself, making it harder for attackers to sneak in their malicious code.
- Secure coding practices - Follow secure coding guidelines like the OWASP Secure Coding Practices to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to injection vulnerabilities.
- Regular security testing - Don’t forget to test your application for injection vulnerabilities regularly, using tools like vulnerability scanners or penetration testing.
A04:2021 - Insecure Design
Insecure design is all about those fundamental design flaws that make an application vulnerable to attacks. There are a few common insecure design patterns that can make your application vulnerable, so let’s check them out:
- Insufficient input validation - If you’re not validating user inputs properly, you’re leaving the door wide open for attackers to send malicious data to your application. This can lead to a whole host of problems, like injection attacks or data leaks.
- Lack of error handling - When your application doesn’t handle errors gracefully, it can leak sensitive information or crash unexpectedly, giving attackers valuable insights into your system’s inner workings.
Best practices to help you design your applications securely from the get-go:
- Security by design approach - Make security a priority throughout the entire development process, from design to deployment. This means thinking about potential threats and vulnerabilities at every stage of the SDLC.
- Threat modeling - Identify and analyze potential threats to your application, and then design countermeasures to mitigate those risks. This helps you stay one step ahead of attackers, ensuring your application is built to withstand their tricks.
- Secure coding guidelines - Follow best practices for secure coding, like the OWASP Secure Coding Practices or your organization’s specific guidelines. This helps ensure your code is free from common security pitfalls that can lead to vulnerabilities.
A05:2021 - Security Misconfiguration
What is a security misconfiguration? It’s when an application isn’t set up properly in terms of security, leaving it vulnerable to exploitation. Here are some of the most common security misconfiguration issues you might run into:
- Default configurations - Using out-of-the-box settings for your application, server, or framework can leave you vulnerable to known exploits. Attackers love defaults, as they often come with weak security settings and can be easily exploited.
- Incomplete or ad-hoc configurations - When you don’t have a comprehensive, well-documented configuration process, it’s easy for security settings to slip through the cracks or be applied inconsistently.
- Unnecessary features - Running unused features, services, or components in your application can create potential attack vectors that you might not even be aware of.
- Outdated components - Failing to keep your software components up to date can expose your application to vulnerabilities and exploits in older versions.
Here’s a few best practices to help you avoid security misconfigurations:
- Comprehensive configuration management - Establish a robust, documented process for configuring your application, servers, and frameworks. This helps ensure that all security settings are applied consistently and nothing slips through the cracks.
- Regularly audit and review configurations - Make a habit of reviewing and auditing your application’s configurations to catch any mistakes or inconsistencies before they become a problem.
- Disable or remove unnecessary features - Streamline your application by disabling or removing any features, services, or components that you don’t need. This helps minimize your attack surface and reduces potential vulnerabilities.
- Stay up to date - Keep your application components and software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps you stay ahead of attackers and keep your app as secure as possible.
A06:2021 - Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Vulnerable and outdated components are all about those pieces of software, libraries, or frameworks that your application relies on but haven’t been kept up to date. Common problems associated with vulnerable and outdated components:
- Known vulnerabilities - When you’re using outdated components, you’re leaving your application open to known vulnerabilities that have already been discovered and documented. It’s like giving attackers a roadmap to exploit your app.
- Legacy components - If you’re using components that are no longer supported or maintained, you’re not going to get the security patches and updates you need to keep your app secure. This can leave you exposed to new threats that emerge over time.
- Compatibility issues - Outdated components can create compatibility problems with newer parts of your application or infrastructure, leading to unexpected security risks or system failures.
The impact on businesses can be significant – vulnerable and outdated components can lead to data breaches, system compromises, and other costly security incidents. Make sure to use the following best practices to keep everything running smoothly and securely:
- Maintain an inventory - Keep a detailed, up-to-date inventory of all the components your application uses, including their versions and any known vulnerabilities. This makes it easier to identify potential issues and prioritize updates. Do some research into Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs).
- Regularly update components - Make a habit of updating your components regularly, following a documented process that includes thorough testing and rollback plans in case of issues.
- Monitor for vulnerabilities - Stay informed about new vulnerabilities and exploits that could affect your components by subscribing to relevant security mailing lists or using automated vulnerability monitoring tools.
- Use supported components - Stick to components that are actively maintained and supported, so you know you’re getting the latest security patches and updates when you need them.
A07:2021 - Identification and Authentication Failures
Identification and authentication failures occur when an application doesn’t properly verify who’s who and who’s allowed to do what. This can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and all sorts of other security issues. Here are some common pitfalls when it comes to identification and authentication:
- Weak or default credentials - Using easily guessable or default credentials is like leaving your front door unlocked – it’s just inviting trouble.
- Insecure password storage - Storing passwords in plaintext or using weak hashing algorithms can make it easy for attackers to steal and crack user credentials.
- Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Relying solely on passwords for authentication leaves your application vulnerable to phishing attacks, credential stuffing, and other exploits.
- Insufficient session management - Failing to manage user sessions securely can allow attackers to hijack sessions, steal cookies, or perform other malicious actions.
The impact on businesses can be severe – identification and authentication failures can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and loss of customer trust. Here are some best practices to help you nail identification and authentication in your application:
- Strong credential policies - Implement and enforce strong credential policies, including password complexity requirements, account lockouts, and password expiration.
- Secure password storage - Store passwords securely using strong, up-to-date hashing algorithms (such as bcrypt or Argon2) and salt your hashes to make them even harder to crack.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of authentication, such as a one-time code or a biometric identifier.
- Robust session management - Securely manage user sessions by using unique session IDs, implementing timeouts, and properly handling session termination.
A08:2021 - Software and Data Integrity Failures
Software and Data Integrity Failures happen when an application doesn’t properly protect its software and data from tampering or corruption. Here are some of the common pitfalls:
- Lack of integrity checks - Failing to verify the integrity of your software and data can leave you open to tampering or unauthorized modifications.
- Insufficient protection for data in transit - Transmitting data over insecure channels can expose it to interception or manipulation by attackers.
- Insecure code and resource handling - Failing to handle code, libraries, or other resources securely can introduce vulnerabilities or allow attackers to inject malicious code.
- Vulnerable third-party components - Using third-party components with known vulnerabilities can compromise the integrity of your entire application.
Consider these best practices to help you maintain software and data integrity in your application:
- Implement integrity checks - Use cryptographic hashes, digital signatures, or other integrity verification methods to ensure your software and data haven’t been tampered with or corrupted.
- Secure data in transit - Use encryption and secure communication protocols (such as TLS) to protect data as it moves between your application and other systems.
- Follow secure coding practices - Use secure coding guidelines, like the OWASP Secure Coding Practices, to ensure your code and resource handling is safe and free from vulnerabilities.
- Vet third-party components - Carefully evaluate third-party components for known vulnerabilities and keep them up to date to minimize potential risks.
A09:2021 - Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
Security Logging and Monitoring Failures occur when an application doesn’t properly record, monitor, or analyze security-related events. This can leave you in the dark about what’s happening in your app and make it harder to detect and respond to security incidents. Here are some common challenges when it comes to logging and monitoring:
- Insufficient logging - Failing to log important security events can make it difficult to understand the context of an incident or identify potential threats.
- Incomplete monitoring - If you’re not monitoring all relevant components of your application, you might miss critical security events or early warning signs of an attack.
- Lack of log analysis - Simply logging events isn’t enough; if you’re not analyzing your logs regularly, you might not spot patterns or trends that indicate a security issue.
- Inadequate alerting and response - Without a proper system for alerting and responding to security events, you may not be able to react quickly enough to contain an incident or prevent further damage.
Improve security logging and monitoring in your application using these best practices:
- Log all relevant events - Make sure you’re logging all important security events, including successful and failed authentication attempts, access control decisions, and data modification actions.
- Monitor your entire application - Keep an eye on all components of your application, from the frontend to the backend, to ensure you’re not missing any critical security events.
- Regularly analyze logs - Make a habit of reviewing and analyzing your security logs to spot patterns, trends, or anomalies that could indicate a security issue.
- Implement effective alerting and response - Establish a robust system for alerting and responding to security events, including clear procedures for escalation and incident management.
A10:2021 - Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Server-Side Request Forgery occurs when an attacker manipulates your application into sending unauthorized requests to internal or external resources. Here are some common scenarios where SSRF happens:
- Lack of input validation - If your application doesn’t properly validate user input, attackers might be able to craft malicious URLs or other data to trigger SSRF.
- Insecure handling of URLs or redirects - Failing to handle URLs or redirects securely can make it easier for attackers to manipulate your application into sending unauthorized requests.
- Exposing internal resources - When your application exposes internal resources (like APIs or databases) to external users, you increase the risk of SSRF attacks.
Here are some best practices to help you prevent SSRF attacks:
- Validate user input - Always validate user input to ensure it’s within expected bounds, and sanitize it to prevent the injection of malicious content.
- Handle URLs and redirects securely - Use a whitelist or a strict allowlist of approved URLs to limit where your application can send requests, and avoid using user input to construct URLs or redirects.
- Limit access to internal resources - Restrict access to internal resources as much as possible, and use secure communication channels (like VPNs or secure APIs) to protect data when it’s transmitted between systems.
- Implement network segmentation - Segment your application infrastructure to limit the potential impact of SSRF attacks and make it harder for attackers to move laterally within your network.
Conclusion
We’ve reached the end of our journey through the OWASP Top 10 2021 vulnerabilities. We’ve covered everything from Broken Access Control to Server-Side Request Forgery, and we hope you’ve picked up some valuable tips and best practices along the way to help keep your applications secure. Remember that the OWASP Top 10 is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to application security. It’s a fantastic starting point, but it’s essential to continuously assess your app’s security posture and keep refining your approach as new challenges arise.
About the Author:
Application Security Engineer and Red-Teamer. Over 15 years of experience in Application Security, Software Engineering and Offensive Security. OSCE3 & OSCP Certified. CTF nerd.